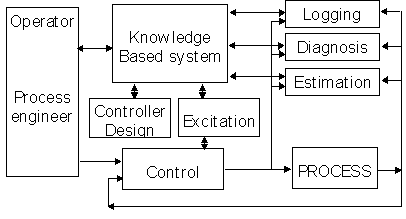
Fig. .5 Expert controller structure proposed in [Årzen, 1995b]
Since its beginning, AI has been present in control and process engineering. At that time AI was focused on learning architectures using connective systems called artificial neural networks. Some structures such as, Perceptron, by Rosenblatt in 1962, and ADALINE, by Widrow in 1962, are two representative examples of these epoch. From then until now, several approaches have succeeded in the AI domain to improve control systems according to two perspectives ; on one hand the techniques that try to mimic the expertise of humans and on the other hand the techniques based on machine learning [Årzen, 1995b]. In spite of the fact that this thesis is centred on the first approach (using expert knowledge to improve control actions and supervise process behaviour), a brief description of these approaches is given :

All of these AI technologies have been tested and applied with success in direct control applications. The difference between applying such technologies in a control strategy or in a supervision structure, is basically the kind of data to be used. Control is performed close to process and, therefore, input and output of controllers are numerical sampled data coming from, usually, one source. Simple numerical features (derivatives, filtering) are obtained from these signals before being processed by the controller. In supervisory systems more significant information must be obtained to be useful for automatic use by AI tools, because they try to identify those signals with structural changes, faults or localised missfunctions. Moreover, qualitative representations of these signals must be managed together with numerical values.Expert systems were originally developed to solve static problems (situations where the premises do not change with time). Consequently , the introduction of ES in the control domain had some difficulties because of the importance of temporal dependencies of dynamic systems where control strategies are applied. Then, normally they are used in a higher level where time dependency is less than in direct control. Expert control falls within this direction and represents an example of how ES can be used for supervision.