2.2 Basic configurations
1.1.1 Basic configurations of computer
systems for supervision
There are several possibilities for basic configuration of the computer
system with respect to the connection to the controlled and supervised
process. A basic common classification is as follows:
-
off-line architecture: in this case the computer is not connected
directly to the process; the input of the data is performed either manually
or through some movable information storage media, as for example magnetic
disks, magnetic tapes, portable PC or specialised computers with relevant
interfaces, etc. This type of architecture is currently mostly out of use
due to the inconvenience and time delay necessary for data loading. However,
in certain specific cases (e.g. collection of data from large amount of
separated unconnected units) or in the case when preliminary human processing
of the data is necessary (e.g. abstract or qualitative information should
be input to the computer, especially if the data should be initially evaluated
with respect to human expert specific, personal knowledge – e.g. taste,
smell, outlook, colour or other hard to measure properties are to be evaluated)
this kind of architecture can still be in use. Further, in case of simulation,
post-processing analysis, and for the purpose of analysis, testing and
research, the off-line architecture is popular thanks to its low cost and
accessibility. Note that the off-line architecture is mostly applicable
for relatively slow, usually man-controlled processes. An important indication
for use of this kind of structure may consist in the fact that the necessary
data sensors and measurement technology does not exist, is unavailable
and/or relies on human or animal senses. Further, it may be the case that
evaluation of selected product properties requires laboratory analyses,
which both must be performed by man and require certain amount of time.
-
in-line architecture: the computer is directly connected to the
process, i.e. there is a physical flow of signals from the process to the
supervising computer. However, there is no possibility to transmit information
from the computer back to the process. This kind of architecture is typical
for the process monitoring systems. It is usually applied at higher
levels of two-level or multiple-level computer controlled systems. The
data coming from the process to the computer is stored, processed and analysed;
the output however is mostly directed towards human operators. The processed
data may be used for various purposes, from warning and alarm generations,
through parameter estimation and display to periodical report generation.
This kind of architecture is mostly applied for processes where direct
reaction of the system is either infeasible or unnecessary, where the relevant
actuators are unavailable or do not exist, or where the reaction cannot
be identified in a unique way and thus the final selection of the operation
is left to the human operator (such situation can take place in Decision
Support Systems (DSS)).
-
on-line architecture: the computer is directly connected to the
process; there is a physical flow of signals from the process to the supervising
computer and simultaneously information is transmitted back from the computer
to the process (and/or to the process controller). This kind of architecture
is most popular in computerised process control systems, including
direct digital control systems and hierarchical control systems. The possibility
to transmit data back to the process allows for closed loop control at
meta-level (e.g. for control algorithm selection or parameter modification),
where the feedback phenomenon assures required performance in case of unexpected
noise. In general, the on-line architecture is most powerful and demonstrates
most interesting possibilities; the signal transformed back to process
and/or its controller can be used for changing set points, control algorithm
paratmetric or structural modification, activation and desactivation of
certain controls, changing the mode and status, modification of process
memory (if relevant), modification and adaptation of models used for optimal
or adaptive control, etc.
The case of on-line control constitutes currently the most frequently
applied type of architecture for control and becomes more and more in use
for supervision. Two further notions, specific for on-line control are:
real-time
systems and any-time systems.
Real time systems constitute a specific class of on-line architectures.
Although there exists no single, precise, widely accepted definition of
such systems, most of the authors accept and put forward the following
characteristics:
-
on-line architecture: the system architecture is of on-line type,
i.e. basing on the received from the process data the computer works out
control and/or decisions which are directly applied to the process,
-
time-critical requirements: the speed of the process requires fast
reaction, i.e. there exists time requirements constraining the maximal
time during which the control and/decision must be supplied back to the
process; for specific situations this deadline time is defined a priori
and can be denoted as td.
-
guaranteed response time: it is assured that the computer system
and operating algorithm is fast enough (both with respect to the hardware
and the software -- applied algorithms), so that the control/decision will
be always computed in apriori defined guaranteed response time or earlier;
for specific situations this maximal response time can be denoted as tr.
-
satisfaction of time constraints: the maximal response time is less
than the deadline time required while generating a response; for specific
situations this condition can be denoted as
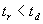
.
In certain more complex systems, the deadline time td
may vary depending on process state, external conditions, noise and current
control goal. Due to very high speed of the modern computers and thanks
to development of diversity of algorithms, it may turn out that a satisfactory
solution is worked out much in advance with respect to required response
time. In such a case the computer system can, using more data, memory,
time and more advanced algorithms, attempt to still improve the solution.
When finally the solution is ultimately required by controlled system,
the last worked out, most optimal solution is returned.
Let 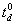 denote the minimal
deadline time for response, i.e. surely no response is required before
denote the minimal
deadline time for response, i.e. surely no response is required before 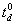 .
Similarly, let
.
Similarly, let 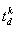 denote the
maximal deadline for response, i.e. certainly, any answer must be provided
before
denote the
maximal deadline for response, i.e. certainly, any answer must be provided
before 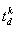 . Thus the first
rough evaluation of the required response time is given by the interval
. Thus the first
rough evaluation of the required response time is given by the interval 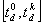 .
Note however, that contrary to the left border, the right border is not
guaranteed. Let
.
Note however, that contrary to the left border, the right border is not
guaranteed. Let 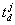 denote
the instant of time varying between
denote
the instant of time varying between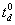 and
and 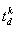 and defining the current
time instant when the answer becomes requested immediately. Further, let
and defining the current
time instant when the answer becomes requested immediately. Further, let 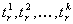 denote the sequence of times necessary to compute the successive solutions,
where
denote the sequence of times necessary to compute the successive solutions,
where 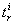 is the time for computing
i-th
solution,
is the time for computing
i-th
solution, 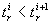 and the i+1
– th solution is better than the i-th one,
and the i+1
– th solution is better than the i-th one, 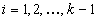 .
For the system working correctly it is necessary to assume that
.
For the system working correctly it is necessary to assume that 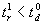 ,
i.e. the first (reactive) solution must be available before the minimal
deadline (as in the case of real-time systems). The further solutions corresponding
to improved quality can be generated later on. When the request for solution
is send to the computer (at
,
i.e. the first (reactive) solution must be available before the minimal
deadline (as in the case of real-time systems). The further solutions corresponding
to improved quality can be generated later on. When the request for solution
is send to the computer (at 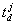 ),
the i-th solution generated at
),
the i-th solution generated at 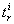 such that
such that 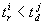 and
and 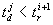 is returned to the system. Since in fact over the whole period when solution
may be requested some solution is ready and waiting for the request, such
system are named any-time systems. Further, it is reasonable to
require that
is returned to the system. Since in fact over the whole period when solution
may be requested some solution is ready and waiting for the request, such
system are named any-time systems. Further, it is reasonable to
require that 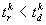 since in the
other case the best algorithm would never be in use.
since in the
other case the best algorithm would never be in use.
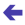
![]() denote the minimal
deadline time for response, i.e. surely no response is required before
denote the minimal
deadline time for response, i.e. surely no response is required before ![]() .
Similarly, let
.
Similarly, let ![]() denote the
maximal deadline for response, i.e. certainly, any answer must be provided
before
denote the
maximal deadline for response, i.e. certainly, any answer must be provided
before ![]() . Thus the first
rough evaluation of the required response time is given by the interval
. Thus the first
rough evaluation of the required response time is given by the interval ![]() .
Note however, that contrary to the left border, the right border is not
guaranteed. Let
.
Note however, that contrary to the left border, the right border is not
guaranteed. Let ![]() denote
the instant of time varying between
denote
the instant of time varying between![]() and
and ![]() and defining the current
time instant when the answer becomes requested immediately. Further, let
and defining the current
time instant when the answer becomes requested immediately. Further, let ![]() denote the sequence of times necessary to compute the successive solutions,
where
denote the sequence of times necessary to compute the successive solutions,
where ![]() is the time for computing
i-th
solution,
is the time for computing
i-th
solution, ![]() and the i+1
– th solution is better than the i-th one,
and the i+1
– th solution is better than the i-th one, ![]() .
For the system working correctly it is necessary to assume that
.
For the system working correctly it is necessary to assume that ![]() ,
i.e. the first (reactive) solution must be available before the minimal
deadline (as in the case of real-time systems). The further solutions corresponding
to improved quality can be generated later on. When the request for solution
is send to the computer (at
,
i.e. the first (reactive) solution must be available before the minimal
deadline (as in the case of real-time systems). The further solutions corresponding
to improved quality can be generated later on. When the request for solution
is send to the computer (at ![]() ),
the i-th solution generated at
),
the i-th solution generated at ![]() such that
such that ![]() and
and ![]() is returned to the system. Since in fact over the whole period when solution
may be requested some solution is ready and waiting for the request, such
system are named any-time systems. Further, it is reasonable to
require that
is returned to the system. Since in fact over the whole period when solution
may be requested some solution is ready and waiting for the request, such
system are named any-time systems. Further, it is reasonable to
require that ![]() since in the
other case the best algorithm would never be in use.
since in the
other case the best algorithm would never be in use.