A Trial Example
In this section we describe in detail one of the trials run in a
scenario of class 4. The environment and the path followed by the
robot are shown in Figure 6.9.
The target landmark in this trial is landmark number 10.
In Figures 6.10 and 6.11 the
incremental building of the map is depicted. They show both a 2D
representation and the topological map actually stored by the
Map Manager. In the topological maps, although not shown,
the arcs have a fixed cost of 1, unless otherwise specified.
Figures 6.12 and 6.13 show the evolution
of the bids of each agent and the Pilot for moving and
looking actions, respectively. In these graphics,
the filled areas indicate the agent that made the highest bid at that
point in time. The corresponding points in Figure
6.9 are also shown.
Next, we comment on the relevant points of the path:
Figure 6.9:
Path followed during the trial. See explanation of
relevant points on the text
|
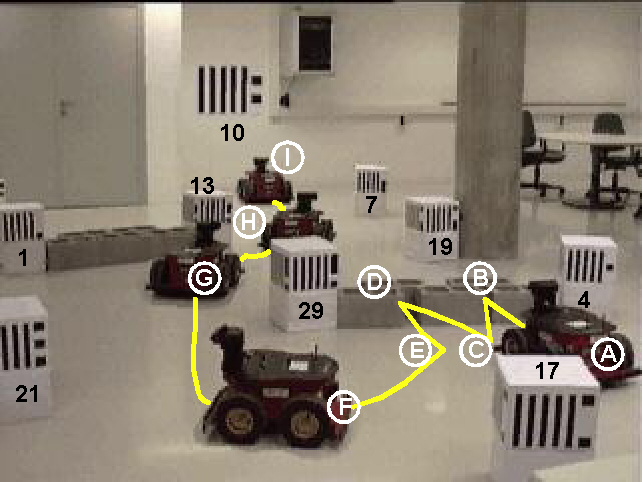 |
Figure 6.10:
Map created during the trial
|
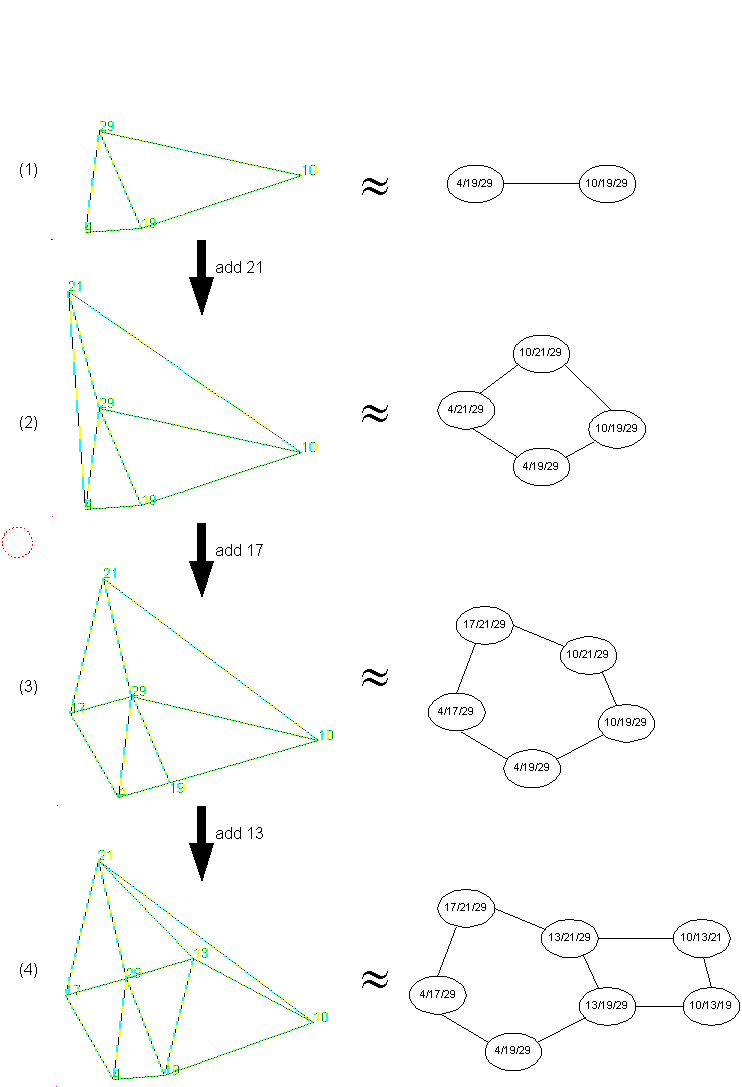 |
Figure 6.11:
Map created during the trial (cont.)
|
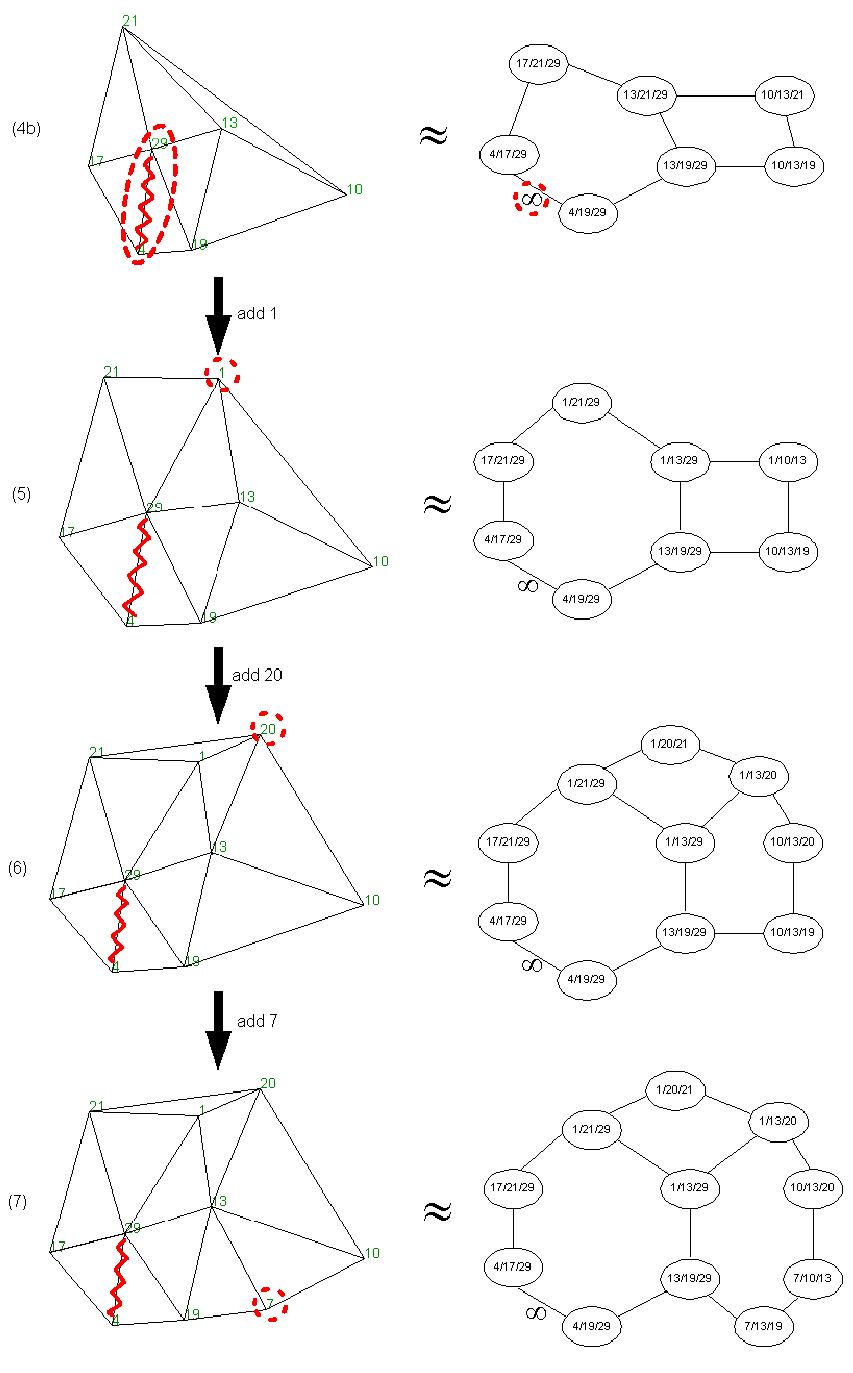 |
Figure 6.12:
Moving bids. Target Tracker in red, and Pilot in green
|
![\includegraphics[width=12cm]{figures/move-filled-rot}](img286.png) |
Figure 6.13:
Looking bids. Target Tracker in red, Pilot in
green and Risk Manager in blue
|
![\includegraphics[width=12cm]{figures/look-filled-rot}](img287.png) |
- A: Starting point of the trial. Initially, landmarks 10,
29 and 19 are visible. With these three landmarks, no map is
created, since at least four landmarks are needed in order to
start building the map.
Landmark 10 is selected as the target by the user and the Rescuer is
informed about it. Then, the Rescuer bids for doing an initial sweep,
as described in Section 4.4.4.
During this sweep,
landmarks 4, 21 and 17 are also identified. With these new
landmarks, the Map Manager is able to start building the
map. The step by step update of the map is shown in Figure
6.10. The corresponding updates after seeing each of these three
landmarks are maps (1) to (3).
When the sweep is finished, the Rescuer informs the
Target Tracker about the target being landmark 10, which
immediately starts bidding for going towards it, and the robot
starts moving.
Actually, the point A in the graphics of the bids corresponds to
this moment, when the Target Tracker starts bidding.
As can be seen in the graphic of moving action bids, the Pilot won
most of the bids. This was so because landmark 4 was close to the robot, and
the Pilot wanted to avoid it.
The trajectory, however, was minimally modified.
Before reaching point B, landmark 13 is identified, and the map is
updated accordingly, resulting in map (4) in Figure 6.10.
- B: The robot bumps into the obstacle between landmarks 29
and 4 and immediately backs up. However, it is not yet considered as
being a long blocking
obstacle, since there is still enough space between the crash point
and landmark 29, through which the robot could pass.
This back up is a built-in action of the Pilot, and it does not bid for
executing it. That is why in the graphic the Target Tracker wins
the bids. However, while the back up action is being executed, these bids
are not taken into account.
- C: After backing up, the Target Tracker bids again for
moving towards the target, but these bids are surpassed by the
Pilot's bids to avoid the just detected obstacle (as can be
seen in the moving bids graphic), and the
trajectory is slightly modified.
- D: The robot bumps again into the obstacle and backs up.
After this second crash,
the obstacle is considered to be blocking the path. The
Pilot informs the Navigation system about the blocking
situation. This information is internally sent to the Map
Manager, which updates the map (the corresponding arc is assigned an
infinite cost, see map (4b) in Figure 6.11), and to the
Rescuer, which asks the Map Manager for a diverting
target. Again, although in the graphics the Target Tracker is
winning the bidding, the back up action is really being executed.
- E: The Map Manager computes the diverting target as
being: ``to cross the edge between landmarks 17 and 29'' and informs the
Rescuer, which will inform the Target Tracker
about the new target. This agent starts bidding to move the robot so that
it crosses the given edge.
- F: At this point, the Target Tracker considers that
the edge 17/29 has been crossed and informs about it. This causes the
Rescuer to set the target to be the original one (landmark 10).
The Target Tracker's bids are again to move towards this landmark.
Before reaching point G, landmarks 1 and 20 are detected and the map
is updated (maps (5) and (6)).
Landmark 20 is not visible in Figure 6.9; it is behind landmark 1.
- G: The proximity of landmark 13 makes the Pilot bid
high to avoid it, surpassing the Target Tracker's bids, and
the robot's trajectory is modified. While avoiding this landmark,
landmark 7 is detected, and the map is updated, resulting in the
final map (7).
- H: At this point the Pilot considers that landmark
13 has been avoided and stops bidding. The Target Tracker
wins again, and it makes the robot go towards the target.
- I: The target is finally reached.
Analyzing the graphic of looking action bids, we can see that the
winning bid is periodically changing between the Pilot and the
Risk Manager. The bids of the Target Tracker are very
low, since the target is precisely located during the whole trial.
Around point H, the bids of the Risk Manager also decay. This
is so because at that point, there are more than six landmarks behind
the robot, which makes the risk 0. The winning bids of the
Target Tracker, at point I, are due to the fact that this agent
bids very high to look towards the target when this has been
reached. The execution of this action has no intention of decreasing the imprecision of the
target's location, but it is just a way to show that it ``knows'' that the target
has been reached.
© 2003 Dídac Busquets